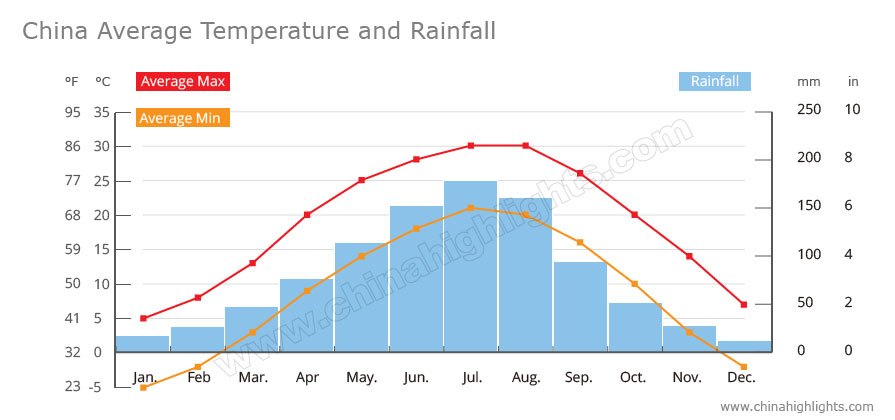
In an average year in a tropical rain forest, the climate is very humid because of all the rainfall, which amounts to about 250 cm per year. The rain forest has lots of rain because it is very hot and wet. That means that there is more direct sunlight hitting the land and sea there than anywhere else.
The sun warms the land and sea and the water evaporates into the air. Then as warm meets cold, condensation takes place and the vapor forms droplets, and clouds form. It rains more than ninety days a year and the strong sun usually shines between the storms. A lot of the rain that falls on the rain forest never reaches the ground. It stays on the trees because the leaves act as a shield, and some rain never gets past the trees to the smaller plants and grounds below.
Trees in this climate reach a height of more than 164 feet. The canopy also keeps sunlight from reaching the plants in the understory. Between the canopy and understory is a lower canopy made up of smaller trees.
Tropical rain forests have a type of tropical climate in which there is no dry season—all months have an average precipitation value of at least 60 mm (2.4 in). There are no distinct wet or dry seasons as rainfall is high throughout the months. Tropical rainforests are defined by the fact that they are hot and wet, typical of tropical climates.
Found near the equator where it is warm, these regions have rainfall year-round, with little to no dry season. The climate of the tropical rainforest biome is perfect for plant and animal growth. The letter code under Köppen's climate classification is Af. The A stands for a place that has a rainy, cool summer but a warm spring.
The f stands for moist, fair rainfall in all months. Af climates are caused by consistent warmth in the temperatures. So, Af stands for the tropical rainforest climate. The Af climates have high humidities, which cause afternoon clouds and rain showers. The average temperature in the coldest month of the year is at least 18° C.
The vegetation for Af is a broad leaf evergreen forest. The location of the Af climate is low-lying areas near the equator. Tropical rainforests cannot thrive in temperatures below 32 degrees Fahrenheit since the plant life is not well-suited to frosty conditions.
On average, tropical rainforests receive annual precipitation of more than 150cm. In a single month, the rainforest can receive 4 inches of rain. Rain forests average around 59 inches of rain per year, and it can rain for days at a time during the wet season.
All tropical rain forests are located in the Southern Hemisphere; therefore, winter occurs from May until September. During this time, temperatures will be at their lowest and rain will likely fall every day. Because of the nearness to the equator (3° southern latitude), the seasonal course knows only low changes in the daylength. Therefore, only drying time and rainy season are distinguished at place of four seasons. Here, a humid-tropical climate rules, that is all year round it is hot and the air is very humid. During the rainy season, from December to May, strong showers come down almost daily.
The amount of precipiation per year reaches more than 2000 millimetres, what corresponds to the double to triple of the value achieved in Germany. At night, the air humidity amounts to at least 95% and is also often very high during the day, so that the air temperature is perceived by people as even warmer than it is actually. The average temperatures of the single months of one year varies only weakly between 26 and 28°C. The maximum temperatures mostly lie between 30 and 40°C, while at night temperatures only reach between 20 and 30°C. Tropical monsoon forests have a climate similar to tropical rainforests, except for rainfall patterns.
Monsoon climates are located along coastal areas, which have different air circulation patterns than those seen in a typical tropical rainforest. Temperatures are comparable between the two, and warm air dominates year-round. The amount of average annual precipitation is also similar between tropical monsoon forests and tropical rainforests. Monsoon forests, however, receive most of their precipitation during the peak of summer, or the monsoon season, due to changes in atmospheric circulation.
In an average year the climate in a tropical rain forest is very humid because of all the rainfall. A tropical rainforest gets about 150 cm of rain per year. It gets lots of rain because it is very hot and wet in rain forests. The hotter the air, the more water vapor it can hold. This is partly due to high levels of cloud cover, which limit the mean number of sunshine hours per day to between four and six.
In hilly areas where air masses rise and cool because of the topography, the hours of sunlight may be even fewer. Nevertheless, the heat may seem extreme owing to the high levels of atmospheric humidity, which usually exceed 50 percent by day and approach 100 percent at night. Exacerbating the discomfort is the fact that winds are usually light; mean wind speeds are generally less than 10 km (6.2 miles) per hour and less than 5 km per hour in many areas. Devastating tropical cyclones occur periodically in some coastal regions toward the margins of the equatorial belt, such as in the West Indies and in parts of the western Pacific region.
Although relatively infrequent, such storms have an important effect on forest structure and regeneration. As tropical rainforests are located on or close to the Equator, the climate is typically warm and wet. The high rainfall and year-round high temperatures are ideal conditions for vegetation growth. The atmosphere in the tropical rainforest is hot and humid as the result of high temperatures and abundance of water. The wide range of plants encourages a huge variety of insects, birds and animals.
Both equatorial and midlatitude regions contain rainforests, and rainforest weather and climate vary by geography. The two primary types of rainforests are tropical and temperate. A third type, the tropical monsoon forest, resembles the tropical rainforest except for the timing of precipitation. In tropical and temperate rainforests, weather patterns follow two primary seasons, wet and dry. Southeast Asia has uniform temperatures, high humidity and lots of rain.
Ninety five degrees Fahrenheit, however, is the high temperature for tropical rainforests. The climate is very humid and sticky because Southeast Asia is surrounded by oceans. The annual precipitation is heavy; 60 inches to over 100 inches. Tropical rainforests are lush and warm all year long! Temperatures don't even change much between night and day.
The average temperature in tropical rainforests ranges from 70 to 85°F (21 to 30°C). The environment is pretty wet in tropical rainforests, maintaining a high humidity of 77% to 88% year-round. The annual precipitation of a rain forest is greater than 150 cm. In only a month the rainforest receives 4 inches of rain.
The rain forest climate is different from a lot of other climates. In other climates, the evaporation is carried away to fall as rain in far off areas, but in the rain forests, 50 percent of the precipitation comes from its own evaporation. A lot of the rain that falls on the rain forest never reaches the ground, instead it stays on the trees because the leaves act as a shield. Statistically, they cover approximately 7% of the surface of the earth.
As its name implies, tropical rainforest experiences a lot of rain during specific seasons, but pleasantly good distribution throughout the year each day and night. Tropical rainforests are extremely vital since the water they generate is evaporated and utilized as rain in other parts of the earth. The principal determining climatic factor for the distribution of rainforests in lowland regions of the tropics, therefore, is rainfall, both the total amount and the seasonal variation.
Soil, human disturbance, and other factors also can be important controlling influences. Savanna is grassland with scattered individual trees. Savannas of one sort or another cover almost half the surface of Africa and large areas of Australia, South America, and India. Climate is the most important factor in creating a savanna.
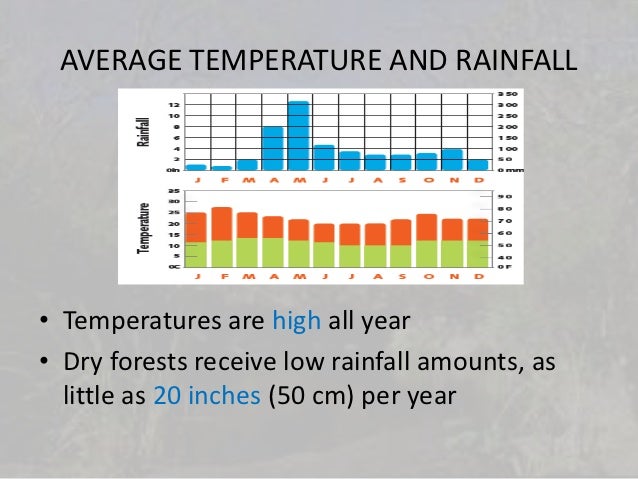
Savannas are always found in warm or hot climates where the annual rainfall is from about 50.8 to 127 cm (20-50 inches) per year. It is crucial that the rainfall is concentrated in six or eight months of the year, followed by a long period of drought when fires can occur.In the summer there is lots of rain. An average of 15 to 25 inches of rain falls during this time.
It gets hot and very humid during the rainy season. The tropical rain forest is a forest of tall trees in a region of year-round warmth. An average of 50 to 260 inches (125 to 660 cm.) of rain falls A tropical rain forest has more kinds of trees than any other area in the world. Produce 40% of Earth's oxygen.Almost all rain forests lie near the equator. There are four very distinct layers of trees in a tropical rain forest.
These layers have been identified as the emergent, upper canopy, understory, and forest floor. The yearly rainfall ranges from 80 to 400 inches , and it can rain hard. Most afternoons experience a heavy downpour, which helps to keep the rainforest moist. All tropical rain forests resemble one another in some ways. Many of the trees have straight trunks that don't branch out for 100 feet or more; there is no sense in growing branches below the canopy where there is little light. The majority of the trees have smooth, thin bark because there is no need to protect the them from water loss and freezing temperatures.
It also makes it difficult for epiphytes and plant parasites to get a hold on the trunks. The bark of different species is so similar that it is difficult to identify a tree by its bark. Many trees can only be identified by their flowers. Temperate rainforests are located in regions such as the northwest portion of the United States, called the Pacific Northwest. Over two-thirds of all temperate rainforests are found in the Pacific Northwest. Mountain ranges protect temperate rainforests from weather extremes, and they typically have moderate weather even though they're located far from the equator.
On average, temperate rainforests will receive less rainfall and have cooler temperatures than their tropical counterparts. Precipitation averages approximately 250 centimeters annually. But it will vary from 150 to 500 centimeters in any given year. The tropical rain forest is classified under the Köppen Classification system as Af, meaning tropical forest.
The Ais given to tropical climates that are moist for all months and which have average temperatures above 18 degrees Celsius. The f stands for sufficient precipitation for all months. The latitude range for my climate is 15° to 25° North and South of the equator. Many of the trees have straight trunks that don't branch out for 100 feet or more. There is no sense in growing branches below the canopy where there is little light. It also makes it difficult for epiphytesand plant parasites to get a hold on the trunks.
Rainforests now cover less than 6% of Earth's land surface. Scientists estimate that more than half of all the world's plant and animal species live in tropical rain forests. Tropical rainforests produce 40% of Earth's oxygen. Microclimate) is moderated by the presence of plant parts that reduce incoming solar radiation and circulation of air. This is particularly true in tropical rainforests, which are structurally more dense and complex than other vegetation. Within the forest, temperature range and wind speed are reduced and humidity is increased relative to the climate above the tree canopy or in nearby clearings.
The equatorial latitude of tropical rainforests and tropical deciduous forests keeps day length and mean temperature fairly constant throughout the year. The sun rises daily to a near-vertical position at noon, ensuring a high level of incoming radiant energy at all seasons. Kuching, the capital of Sarawak, is moderately hot, but very humid at times and receives substantial rainfall.
Kuching is the wettest populated area in Malaysia with an average of 247 rainy days per year. The wettest times are during the Northeast Monsoon months of November to February, and the "dry" season is from June until August. Temperatures in Kuching range from 66°F to 97°F, and the average temperature is around 73°F in the early hours of the morning, which rises to around 91°F during mid-afternoon. The heat index often reaches 108°F during the dry season due to the humidity.
Tropical rainforests are warm and humid—the temperature ranges from 21 to 30 degrees Celsius (70 to 85°F). The average annual temperature of tropical rainforests is above 20 °C. A tropical rainforest climate or equatorial climate is a tropical climate usually found within 10 to 15 degrees latitude of the equator. They experience high mean annual temperatures, small temperature ranges, and rain that falls throughout the year.
























No comments:
Post a Comment
Note: Only a member of this blog may post a comment.